
[DIAGRAM] Diagram Of Nephron
2. The "Bowman's capsule" is the part of a nephron which receives the filtrate. It is a part of a nephron, and only delivers filtrate to a single nephron. The afferent artery and efferent artery are not nephrons, they are arteries outside the nephron that run around the kidney (the red lines that run around the large kidney diagram to the right.

A human nephron, showing the anatomic location of the distal tubule.... Download Scientific
Figure 25.4. 25.4.: Aquaporin Water Channel. Positive charges inside the channel prevent the leakage of electrolytes across the cell membrane, while allowing water to move due to osmosis. The functional unit of the kidney, the nephron, consists of the renal corpuscle, PCT, loop of Henle, and DCT.
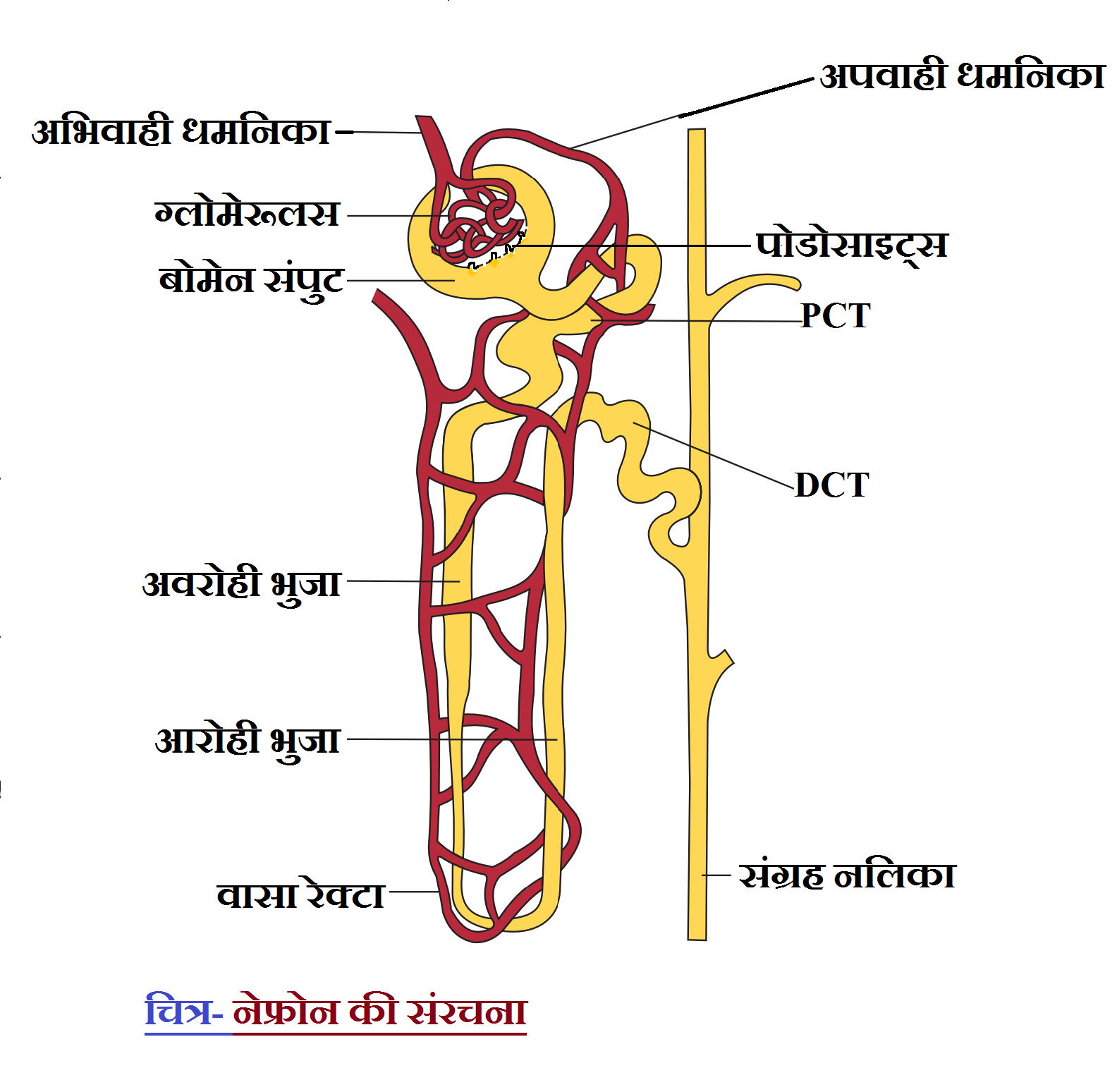
Nephron structure and function नेफ्रोन की संरचना तथा कार्य NCERT SCIENCE IN HINDI
A nephron is the basic unit of structure in the kidney. A nephron is used separate to water, ions and small molecules from the blood, filter out wastes and toxins, and return needed molecules to the blood. The nephron functions through ultrafiltration.
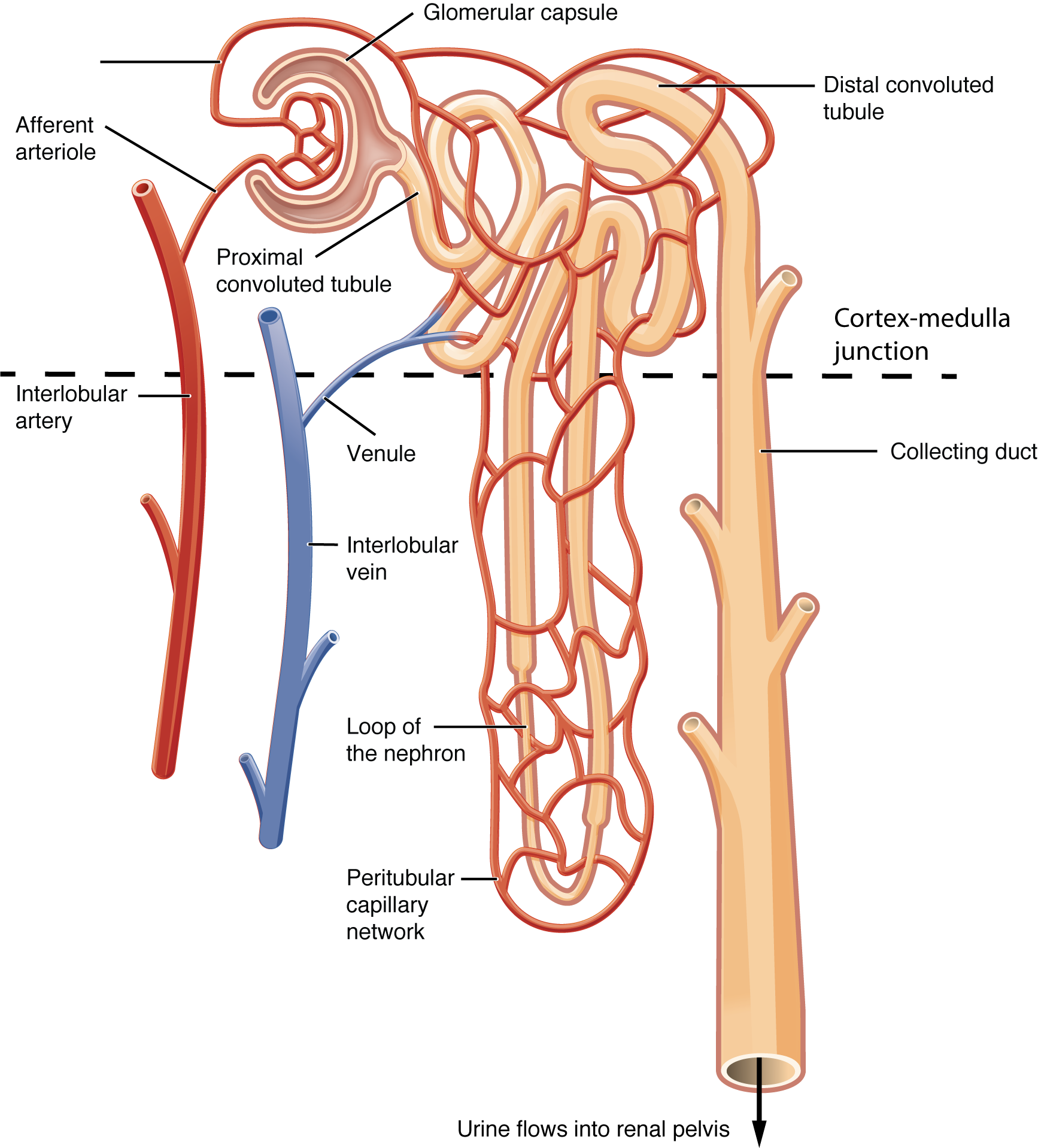
Nephron What is the Structure and its Functions of Nephron?
nephronophthisis tissue clearing Translational Statement The kidney maintains body homeostasis via its complex 3-dimensional (3D) nephron structure. When this structural organization is altered, renal pathophysiology ensues. Chronic kidney diseases are characterized by the development of renal lesions.

Nephron Definition, Structure, Physiology, Functions
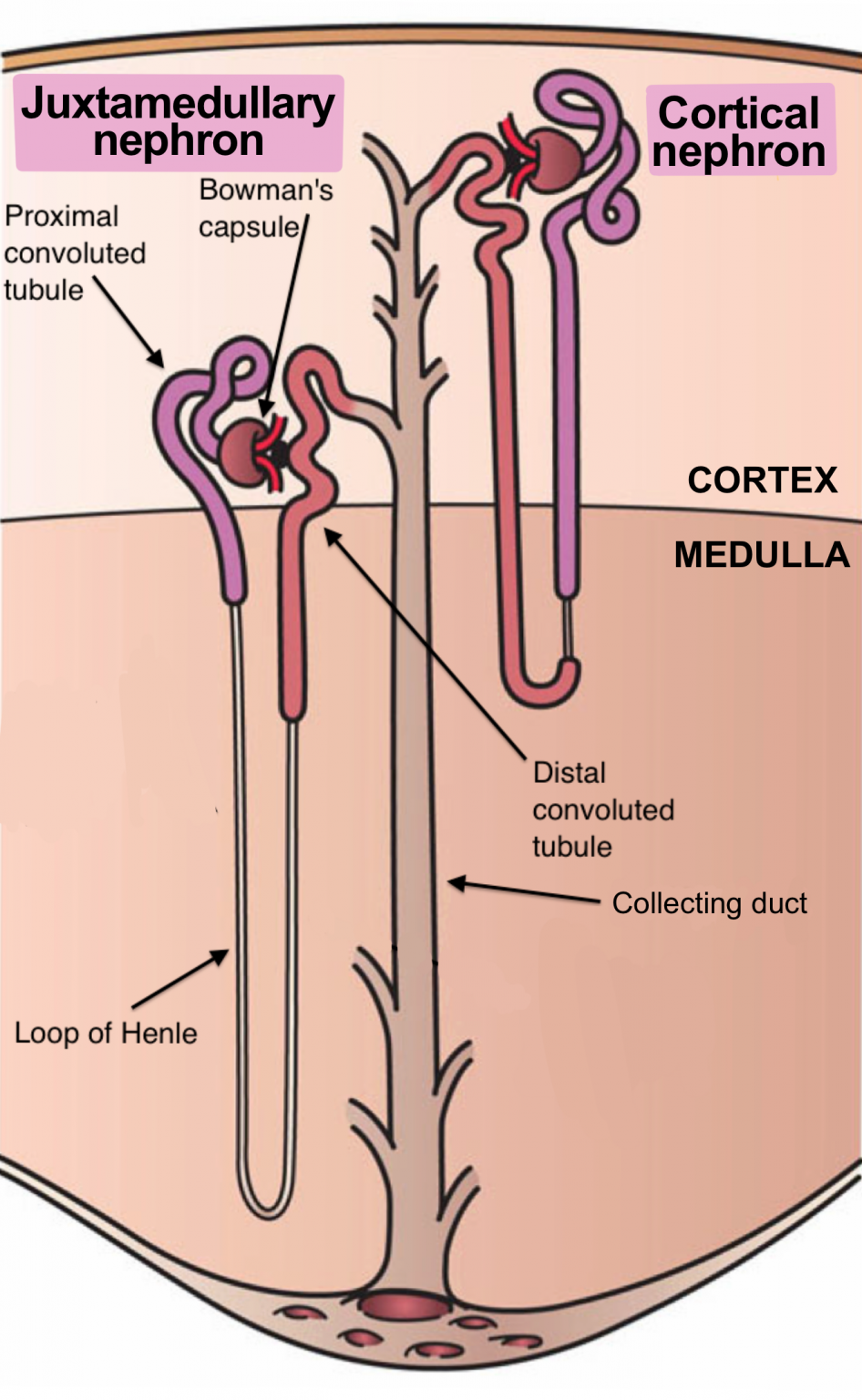
Figure 1. The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney. The glomerulus and convoluted tubules are located in the kidney cortex, while collecting ducts are located in the pyramids of the medulla. (credit: modification of work by NIDDK) Tubular parts of a Nephron - converts the filtrate into urine The Bowman's capsule / Glomerular capsule:

Diagram of the nephron segments and its juxtaglomerular apparatus Download Scientific Diagram
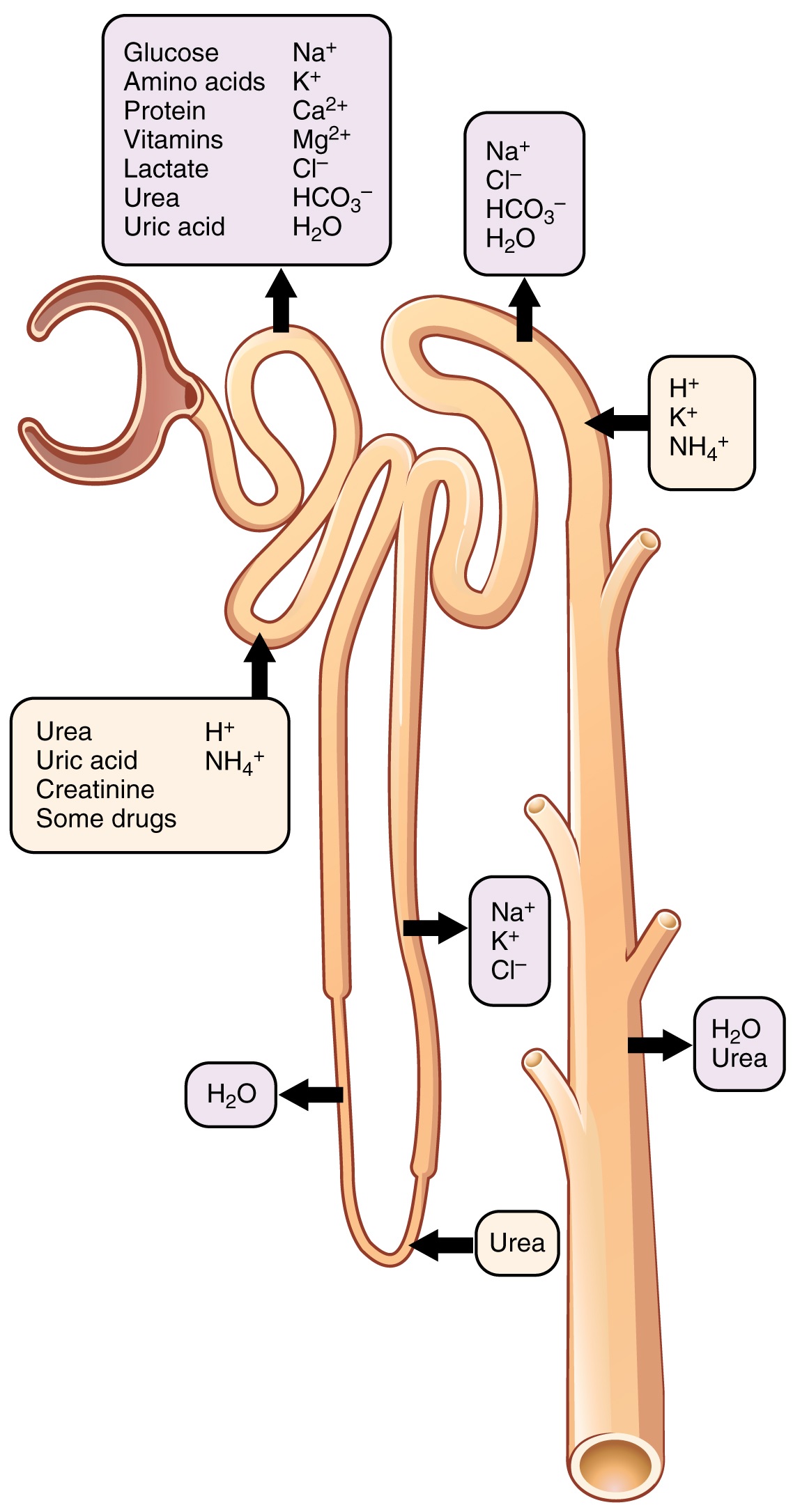
Figure 57.5 Nephron anatomy. Filtrate from Bowman's capsule enters renal tubule Made up of proximal convoluted tubule, descending/ascending limbs of nephron loop (loop of Henle), distal convoluted tubule, collection ducts (which send urine to minor calyces) Filtrate is further filtered by passing water, solutes between filtrate, blood in peritubular capillaries Blood pressure, glomerular.
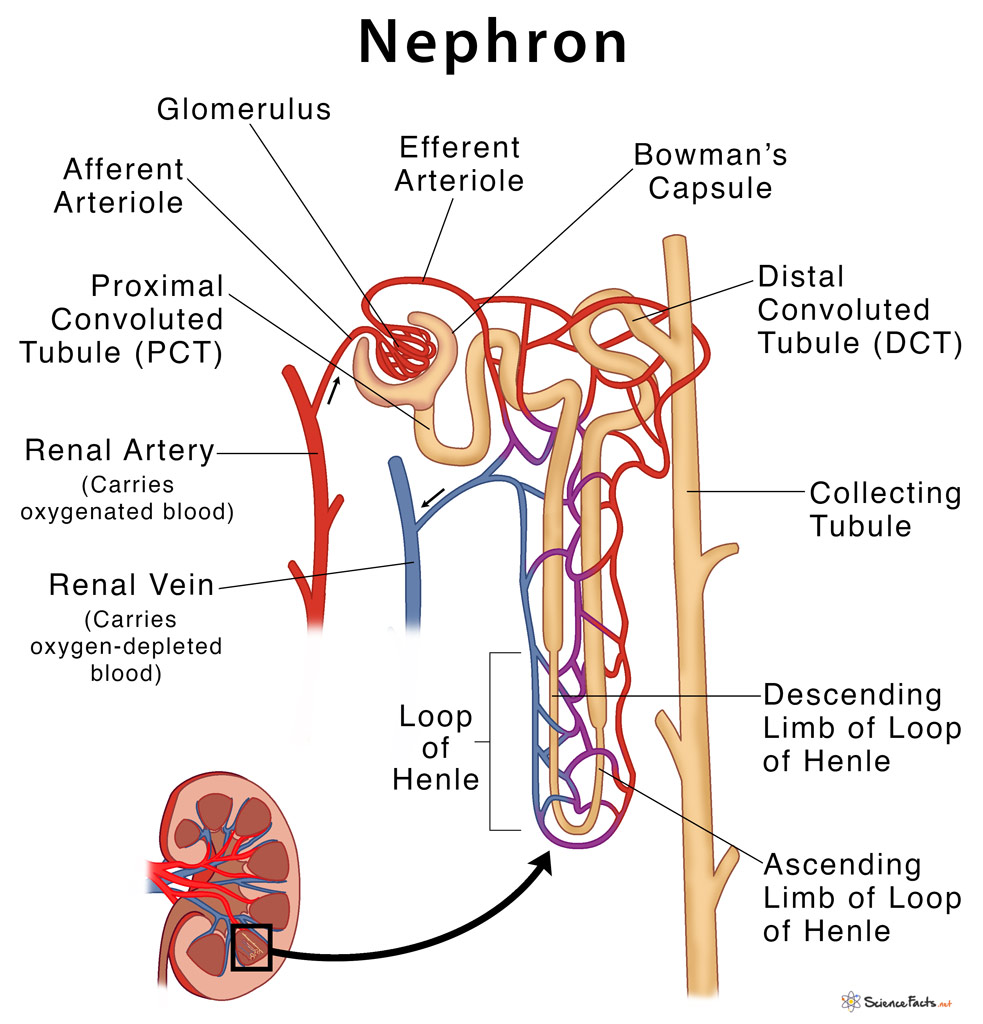
Nephron Definition, Parts, Structure, & Functions, with Diagram
Nephren-Ka, "The Black Pharaoh" (also called Nophru-Ka) is a fictional pharaoh of Ancient Egypt, invented by H. P. Lovecraft, who depicted him as a worshipper of the Outer God Nyarlathotep. Later versions of the Cthulhu Mythos presented him as an avatar of Nyarlathotep himself. Contents 1 In Lovecraft's Fiction 2 Appearance 3 Cult 4 History

The Nephron Simple Structure and Function of Kidney
Structure Fig.1) Schematic diagram of the nephron (yellow), relevant circulation (red/blue), and the four methods of altering the filtrate. The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney. [2] This means that each separate nephron is where the main work of the kidney is performed. A nephron is made of two parts:

Nephron anatomy. The nephrons are made up of tubules, and the proximal... Download Scientific
Gross Anatomy. Each kidney is convex laterally and concave medially with a medial indentation called the hilum. Blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, nerves, and the ureter enter or exit at the hilum. An adult kidney is about 12 cm long, 7 cm wide, and 2.5 cm thick. The internal macroscopic anatomy of a kidney is best observed in frontal section.

Functional Anatomy of the Kidney Organization of the Urinary System The Urinary System
Category: Science & Tech Related Topics: loop of Henle On the Web: See all related content → nephron, functional unit of the kidney, the structure that actually produces urine in the process of removing waste and excess substances from the blood. There are about 1,000,000 nephrons in each human kidney.

Simple Diagram Of Nephron
The left kidney is located at about the T12 to L3 vertebrae, whereas the right is lower due to slight displacement by the liver. Upper portions of the kidneys are somewhat protected by the eleventh and twelfth ribs ( Figure 25.7 ). Each kidney weighs about 125-175 g in males and 115-155 g in females. They are about 11-14 cm in length, 6.
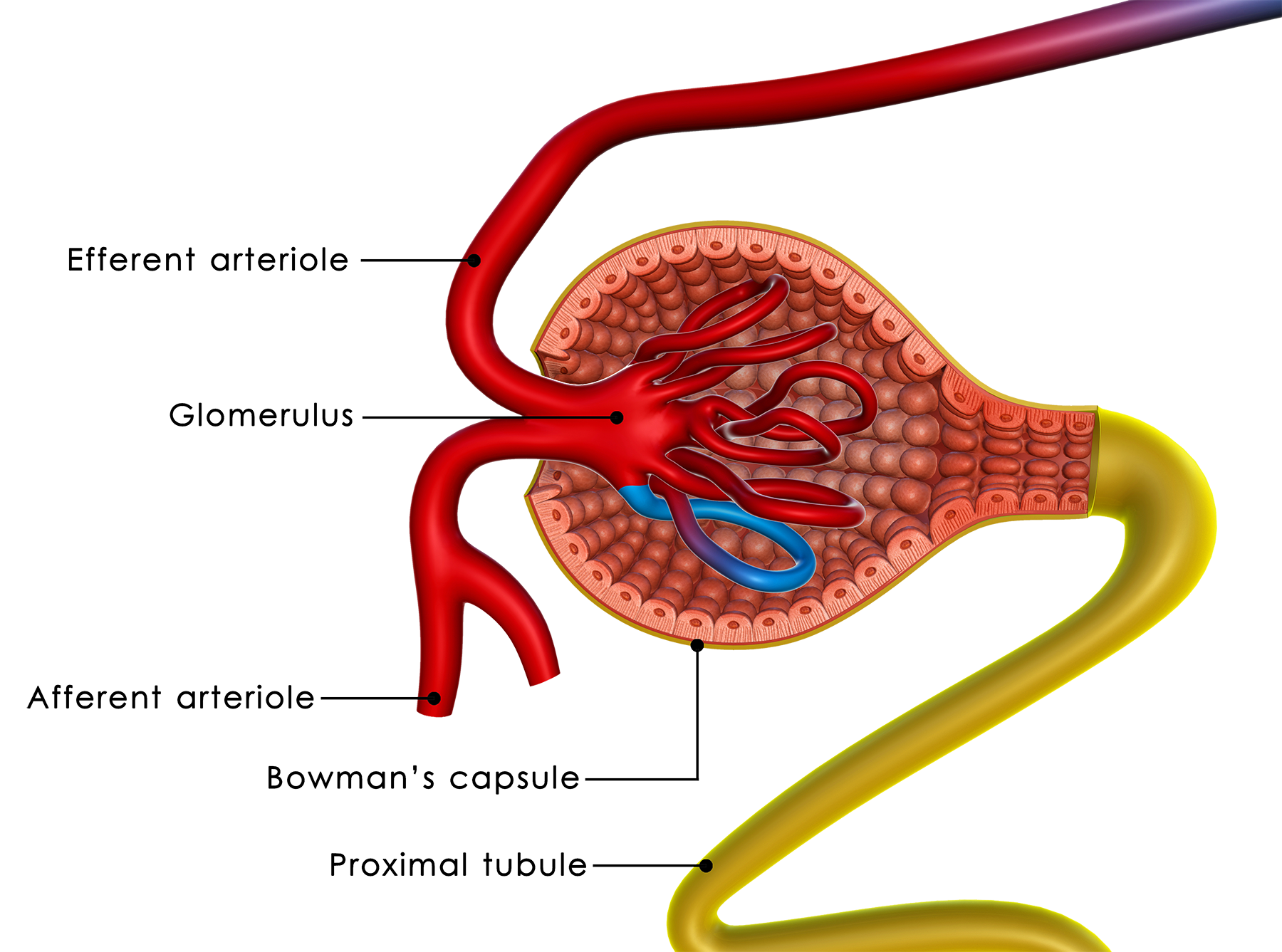
The Structure and Function of the Nephron Made Easy InteractiveBiology
Nephrons are the "functional units" of the kidney; they cleanse the blood of toxins and balance the constituents of the circulation to homeostatic set points through the processes of filtration, reabsorption, and secretion.
Kidney Basic Function and Anatomy Human Physiology
Renal Corpuscle. The renal corpuscle can be found in figure 4 and consists of the glomerulus (a high-pressure capillary bed) surrounded by the Bowman's capsule (the first section of the nephron tubule). Afferent arterioles lead into the glomerulus, and efferent arterioles lead away from the glomerulus which can be seen in figure 4.The Bowman's capsule captures and directs filtrate from the.

Schematic representation of the nephron. There are two types of... Download Scientific Diagram
Each part of the nephron (seen in Figure 1) performs a different function in filtering waste and maintaining homeostatic balance. The glomerulus forces small solutes out of the blood by pressure. The proximal convoluted tubule reabsorbs ions, water, and nutrients from the filtrate into the interstitial fluid, and actively transports toxins and drugs from the interstitial fluid into the filtrate.

Showing the labeled diagram of human nephron adapted from... Download Scientific Diagram
Renal pathologies can be grossly categorized depending on the affected segment of the nephron: the glomerulus, tubules, interstitium, or blood supply. Each one differs in clinical manifestations, making it vital for the clinician to integrate differential diagnoses.
Structure and Functions of Nephron
A nephron is the basic structural and functional unit of the kidneys that regulates water and soluble substances in the blood by filtering the blood, reabsorbing what is needed, and excreting the rest as urine. Its function is vital for homeostasis of blood volume, blood pressure, and plasma osmolarity. It is regulated by the neuroendocrine.